Have you noticed how quickly digital commerce is evolving, and how businesses are redefining customer experiences? Companies that once depended on rigid platforms are now exploring models such as headless commerce and composable commerce to build flexible and scalable online ecosystems. This shift is not simply a technology upgrade, it is a response to the rising expectations of today’s digital-first customers.
In the early years of eCommerce, platforms were developed as single, all-in-one solutions. While these systems served their purpose, they lacked the agility to support new business models or deliver seamless omnichannel experiences. As consumer behavior became more complex, businesses required an approach that could adapt quickly to changing market demands.
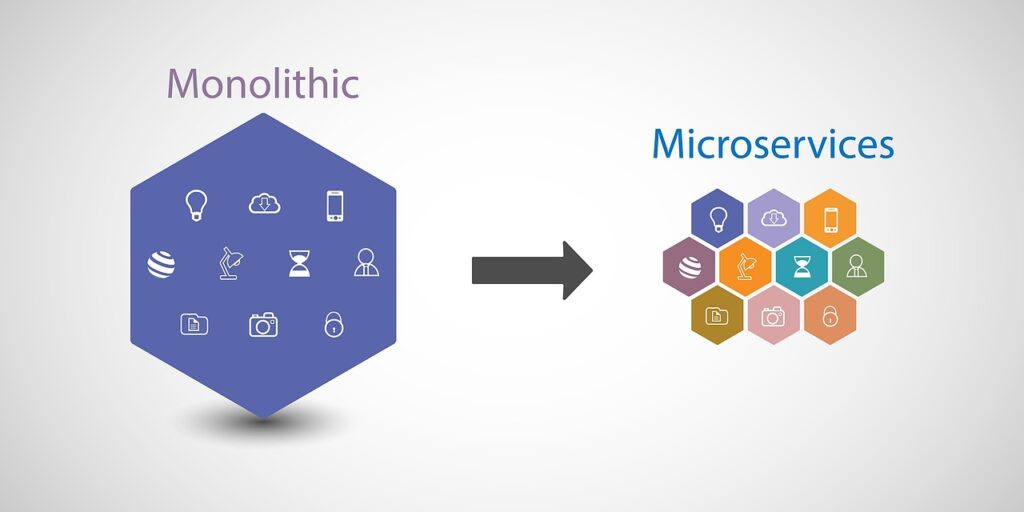
This transformation introduced the concept of decoupled commerce architecture, where the front-end presentation layer is separated from the back-end commerce engine. By moving away from tightly coupled monolithic architecture, organizations gained the ability to innovate on customer-facing experiences while keeping the core operations stable.
Gartner predicts that by 2023 organizations that adopt a composable commerce approach will outpace competition by 80% in the speed of new feature implementation. This insight highlights how modular commerce strategies are becoming essential for companies seeking agility and innovation.
The adoption of decoupled systems created the foundation for two influential models: headless commerce and composable commerce. Both extend the benefits of separation, but they differ in scope, scalability, and flexibility. As a result, companies today can choose between these architectures based on their long-term vision, innovation goals, and growth strategy.
What is Headless Commerce?
The fundamental concept of headless commerce involves the separation of the frontend from the backend, allowing them to operate independently.
- Frontend: The frontend is solely responsible for managing the presentation part of the website.
- Backend: The backend is tasked with handling operational aspects, such as order processing and inventory management. This separation leads to cleaner code, allowing both parts to be worked on concurrently without affecting each other
- Communication Mechanism (APIs): Communication between the frontend and backend is primarily facilitated by APIs (Application Programming Interfaces).
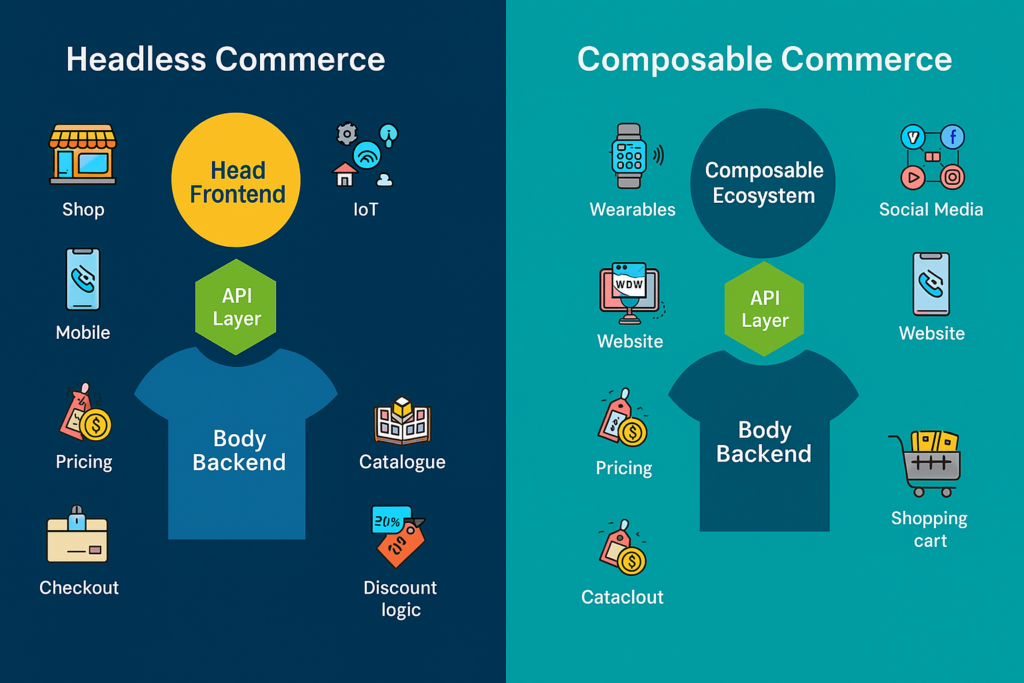
Headless vs. Monolithic Solutions
Aspect | Monolithic Solutions | Headless Solutions |
Architecture | Frontend and backend are tightly coupled, making setup simple but rigid. | Frontend and backend are decoupled, allowing independent operations and flexibility. |
Ease of Setup | Easy to set up and manage, even with minimal technical expertise. | Requires technical expertise to integrate APIs and manage frontend-backend connections. |
Flexibility | Limited flexibility, as updates require redeploying the whole application. | High flexibility, enabling tailored frontends and custom customer experience. |
Scalability | Challenging to scale due to rigid architecture. | Scales easily by adding or replacing services without disrupting the system. |
Performance | May struggle with speed as the system grows. | Enhanced performance with faster load times and optimized user journeys. |
Cost | Generally cheaper, ideal for smaller businesses or projects. | Higher upfront investment with ongoing costs for APIs, hosting, and integrations. |
Examples | WooCommerce, BigCommerce (historically monolithic). | Shopify (headless implementations), Adobe Commerce, commercetools. |
A 2022 Forrester study found that 41 percent of companies using headless commerce launched new experiences faster than those relying on traditional systems. The benefits of headless commerce include faster updates and improved scalability. This flexibility creates a future-proof headless commerce model that adapts as customer needs and technologies evolve.
What is Composable Commerce?
Composable commerce is a modular, API-first approach where businesses integrate best-of-breed services to build their commerce stack. Unlike headless, which separates only the front-end, composable allows companies to choose individual components such as payment, search, or personalization and connect them like building blocks.
This flexibility is based on MACH principles: Microservices, API-first, Cloud-native, and Headless.
- Microservices: Breaking down complex applications into small, independent, and loosely coupled services (e.g., a separate service for product catalog, checkout, search, or inventory).
- API-first: Every service is exposed via APIs, ensuring seamless communication and integration.
- Cloud-native: Designed to run efficiently in the cloud, leveraging scalability and elasticity.
- Headless: Decoupling the front-end from the back-end, as described above.
Imagine building with LEGO bricks instead of buying a pre-assembled LEGO set. Composable commerce allows businesses to select “best-of-breed” components from various vendors – a powerful search tool like Algolia, a flexible Content Management System (CMS) like Contentful or Sanity, a specialized payment gateway, or a personalized recommendation engine. These components are then “composed” together to create a unique, highly tailored e-commerce ecosystem. This approach offers unparalleled customization and avoids vendor lock-in, as components can be swapped out or upgraded independently.
The benefits of composable commerce go beyond flexibility. It enables companies to select specialized tools instead of relying on a fixed platform. This creates a system that is easier to upgrade, integrates smoothly with new technologies, and supports future growth.
Key advantages of a composable commerce solution include:
- Faster adoption of new digital tools
- Stronger personalization and customer engagement
- Better scalability for global markets
- Reduced dependency on a single vendor
For enterprises aiming at agility and long-term value, composable commerce solutions offer a future-ready path that balances speed with innovation.
Headless vs Composable Commerce: The Core Differences
The discussion of composable commerce vs headless commerce highlights a major shift in digital retail. While headless separates the front-end from the back-end, composable takes it further by allowing organizations to integrate best-of-breed solutions such as payments, search, and personalization into a flexible stack.
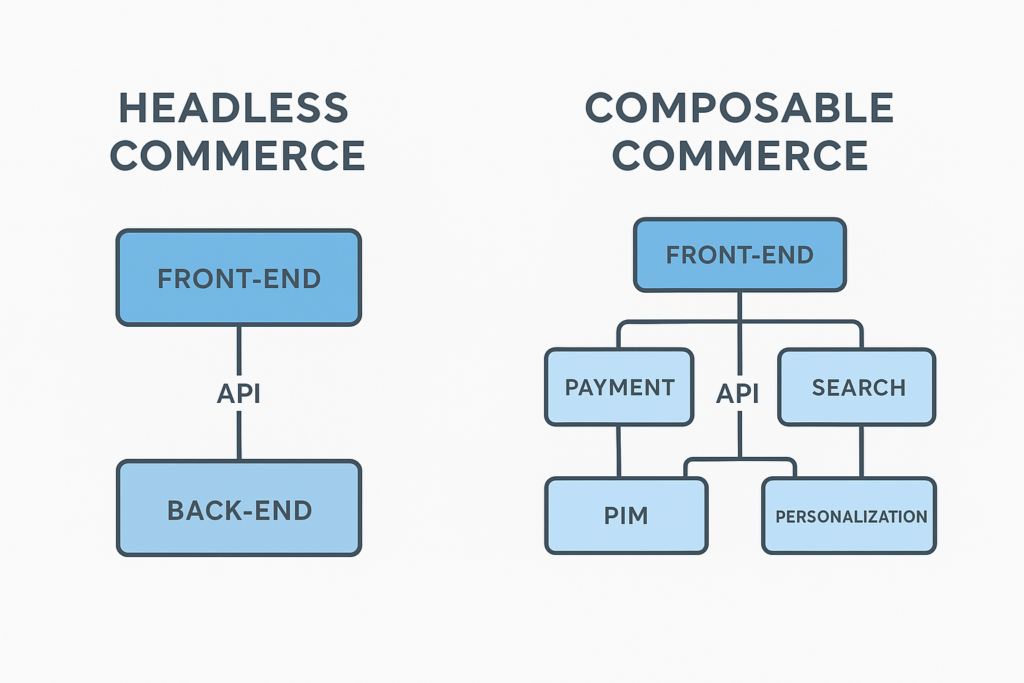
The difference in flexibility is significant. Headless enables custom storefronts, while composable allows companies to plug in the best tools for payments, product information, search, or personalization. This makes composable more adaptable to evolving customer expectations.
Here is a structured view of the differences:
Aspect | Headless Commerce | Composable Commerce |
Architecture | Decoupled front-end and back-end | Modular ecosystem of independent services |
Flexibility | Front-end freedom | Full-stack flexibility with interchangeable tools |
Scalability | Limited by single back-end | High, with rapid integration and innovation |
Best Use Case | Quick redesigns, budget-conscious growth | Global expansion, advanced personalization |
Both headless commerce solutions and composable setups provide growth opportunities, but the right choice depends on long-term goals.
Why Composable Commerce is Gaining Momentum
The rise of composable commerce reflects a shift away from rigid monolithic platforms toward more flexible and scalable architectures. Its momentum can be explained through five key drivers:
-
Speed and Agility
With composable commerce, a business can swap out an outdated search function for an AI-powered one, or integrate a new loyalty program, without a full-scale replatforming project. This speed allows brands to react to market trends, test new ideas, and launch features up to 80% faster than their monolithic counterparts.
-
Best-of-Breed Solutions
Instead of being locked into a single vendor’s tools, composable commerce lets you build your ideal tech stack. You can pick and integrate the best content management, personalization, or payment solutions from different vendors to create a highly optimized ecosystem.
-
Seamless Customer Experience
By separating the front end from the back end (headless architecture), composable commerce gives you the freedom to create unique, personalized experiences on any device, from a website to an in-store kiosk without limitations.
-
Scalability and Efficiency
Unlike monolithic platforms that force you to scale the entire system, composable commerce lets you scale only the specific services under heavy load, like the checkout during a sale. This improves performance and cuts costs.
-
Future-Proofing and Reduced Vendor Lock-in
The modular nature of composable commerce allows you to easily swap out or add new components as technology evolves. This means you can adopt new innovations like AI and AR without a major, costly replatforming project.
Practical Considerations for Choosing the Right eCommerce Architecture
When selecting a commerce approach, many organizations explore headless commerce technology to separate front-end experiences from back-end systems. This allows design freedom and faster updates, but it may still depend on a single system.
Factor | Details |
Cost & Pricing |
|
Security |
|
Provider Reliability |
|
Technical Expertise |
|
Planning & Design |
|
API Credential Security |
|
Documentation & SDKs |
|
Flexibility in Switching |
|
Ultimately, practical considerations like pricing transparency, security measures, and vendor trustworthiness determine whether headless commerce or composable commerce becomes a sustainable long-term strategy. Businesses that align these factors with their growth roadmap are better positioned to unlock agility without unnecessary risks.
Case Examples: Headless and Composable Commerce Implementations
With headless and composable commerce transforming the way businesses deliver customer experiences, many are moving away from traditional platforms. Below are key case studies showcasing these innovative approaches.
Composable Commerce
Serena & Lily
- A U.S. home interior retailer transitioned from a monolithic setup to a composable architecture. By leveraging an API-first, modular design, they addressed complex product configurations and SKU management challenges.
- Impact: Enhanced scalability, dynamic bundling capabilities, and better handling of product variants for a more personalized experience.
Jenson USA
- This U.S. online bicycle retailer adopted composable commerce solutions to improve search customization and personalized customer interactions.
- Results: Increased sales and conversion rates due to tailored search results and targeted marketing efforts.
Headless Commerce Implementations
Yeti Cycles
- Based in Colorado, Yeti Cycles moved to a headless platform using BigCommerce with a Nuxt.js front-end and managed their content with a headless CMS.
- Results: Able to launch new product campaigns in days instead of weeks. The ARC 35th Anniversary bike launch sold out in just 2 hours, generating over 85,000 page views and 38,000 sessions.
Lilly Pulitzer
- U.S. fashion brand Lilly Pulitzer adopted a headless architecture with Progressive Web Apps on Salesforce Commerce Cloud to enhance the mobile experience.
- Outcomes: Mobile traffic jumped by 80% and mobile-generated revenue increased by 33%.
Target
- Major U.S. retailer Target implemented a headless strategy to unify the shopping experience across devices.
- Benefits: Improved conversion rates, streamlined content updates, and reduced operational costs.
Peloton
- The fitness brand Peloton embraced headless commerce to speed up development cycles and enable personalized interactions.
- Results: 40% reduction in development time and a 15% boost in customer retention through personalized content.
Summary Table
Approach | Brand | Implementation Focus | Key Results |
Composable Commerce | Serena & Lily | API-first, modular for complex SKUs | Improved scalability, dynamic product bundling |
| Jenson USA | Personalized search and experience | Higher sales and conversion through tailored customer journeys | |
Headless Commerce | Yeti Cycles | BigCommerce + Nuxt.js + headless CMS | Rapid product launches, high engagement and conversions |
| Lilly Pulitzer | PWA headless on Salesforce Cloud | +80% mobile traffic, +33% mobile revenue | |
| Target | Unified multi-channel experience | Improved conversions, efficiency, lower costs | |
| Peloton | Modular feature rollout | 40% faster development, +15% retention via personalization |
Why This Matters
- Composable Commerce works well for U.S. retailers with complex products, SKU variations, or businesses that need highly tailored shopping experiences.
- Headless Commerce delivers performance improvements, faster content deployment, and superior mobile or omnichannel user experiences, making it ideal for fast-moving U.S. brands.
Choosing the Right eCommerce Tech Stack
A well-structured eCommerce Tech Stack is the foundation of any successful digital commerce strategy. In the context of composable commerce technology, selecting the right tools and platforms ensures scalability, flexibility, and seamless integration across customer touchpoints.
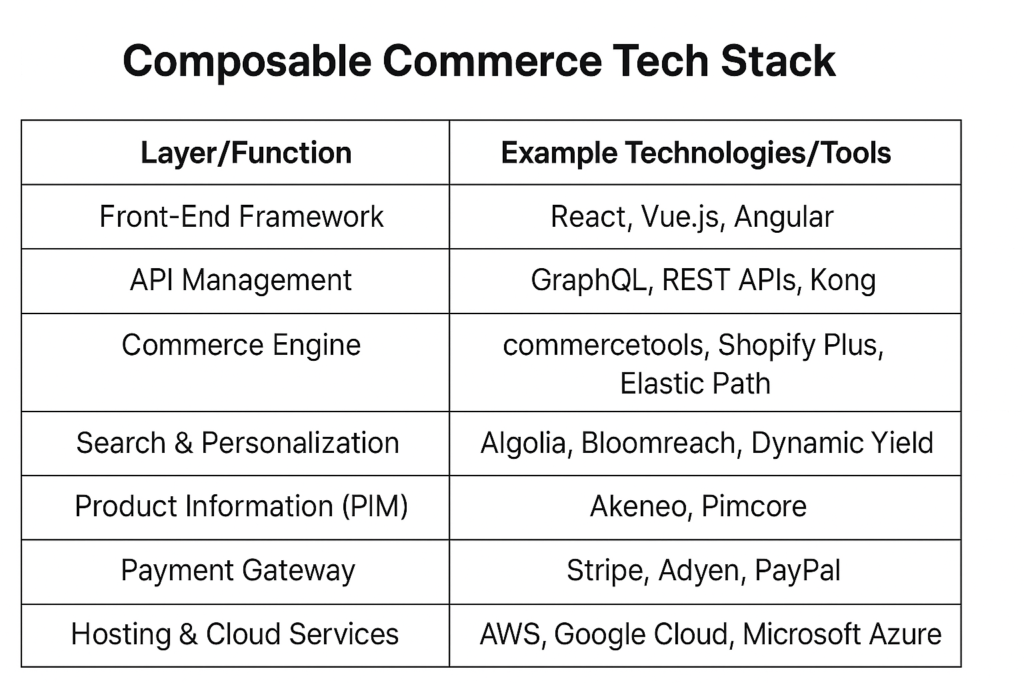
By combining these tools into a composable setup, businesses gain the ability to swap or upgrade individual components without disrupting the entire system. This modularity makes the tech stack future-ready and aligned with evolving customer needs.
Key Trends Shaping the Future of Commerce Architectures
- Evolutionary Trend: The shift from monolithic to headless commerce solutions continues, driven by the demand for scalability, agility, and improved user experience.
- AI Integration: Retailers are using AI to deliver real-time recommendations and tailored shopping journeys.
- API-First Approach: APIs remain central, enabling flexible integrations, rapid innovation, and seamless connections with third-party services.
- Advancements in Headless Frontends: BigCommerce Catalyst, built with Next.js, React server components, GraphQL, and Tailwind CSS, showcases the next phase of headless commerce solutions with structured, deployable storefronts.
- Omnichannel Integration: Unified experiences across web, mobile, social platforms, marketplaces, and physical stores.
- Composable Microservices: Independent modules can be updated or replaced without disrupting other functions, supporting the growth of modern composable commerce technology.
- Cloud-Migration: Cloud infrastructure ensures faster load times, better uptime, and smoother scalability.
- Visual Editing Tools: BigCommerce’s Makeswift adds accessibility by allowing non-developers to manage Catalyst storefronts with visual editing.
- Community-Driven Development: Open-source initiatives like Catalyst evolve through community contributions, ensuring adaptability and long-term sustainability in composable commerce technology.
- GraphQL Adoption: GraphQL is gaining traction due to better documentation and efficient API interactions compared to REST.
- Modularity: Both headless and composable approaches increasingly favor modular integrations, allowing businesses to adopt best-of-breed tools such as search, payment, and personalization.
SparxIT’s Take on the Future of Composable Commerce vs MACH Architecture
At SparxIT, we view MACH (Microservices, API-first, Cloud-native, Headless) as the foundation for agility and modularity, while Composable Commerce extends it by letting businesses integrate best-fit services like payments, search, or checkout. Together, they create a powerful framework for modern digital commerce.
For eCommerce web development, this approach delivers:
- Flexibility to design tailored storefronts and mobile apps
- Scalability to manage global growth
- Faster innovation through easy third-party integrations
- Secure API-driven transactions
- Future readiness for adopting new technologies
Composable Commerce powered by MACH is more than a technical shift. It is a strategic path to building future-ready eCommerce apps that combine agility, speed, and superior customer experiences.

Partner with Experts
Frequently Asked Questions
How does composable commerce differ from traditional eCommerce?







Traditional e-commerce platforms are usually monolithic and rigid, which makes scaling and customization difficult. Composable commerce provides flexibility through modular integrations, enabling faster innovation and easier system upgrades.
What industries can benefit the most from composable commerce?












Industries such as retail, fashion, consumer electronics, and B2B are highly benefited, as these sectors depend on personalization, scalability, and seamless customer engagement.
What are the key benefits of adopting a composable commerce model?












Agility, scalability, and cost efficiency are recognized as the primary benefits. Businesses are able to personalize experiences, adopt best-of-breed tools, and respond to market changes with greater speed.
How can headless commerce improve site performance and user experience?












Headless commerce improves performance by enabling faster page load times, smoother navigation, and tailored digital experiences. The separation of layers ensures that the user interface can be optimized independently for better results.
What is the future of eCommerce with composable commerce?












The future of e-commerce is expected to be driven by composable commerce, as modular ecosystems support continuous innovation, integration of advanced technologies, and future-proof growth in eCommerce website development.


