Cloud platforms today run faster, scale smarter, and cost less than traditional IT setups. At the core of this shift lies virtualization in cloud computing, a technology that transforms physical hardware into flexible, on-demand virtual resources. It is the backbone of modern cloud infrastructure, which enables organizations to run multiple workloads efficiently without being tied to specific hardware.
As businesses move away from rigid on-premise systems, cloud computing virtualization makes scalability, cost optimization, and operational flexibility possible. By pooling resources, dynamically allocating them, and scaling as needed, virtualization helps companies respond quickly to changing workloads while keeping infrastructure costs under control.
In this blog, you will learn what virtualization in cloud computing really means, how cloud virtualization works, and why it is essential for today’s digital environments. We will explore different levels and types of virtualization, key benefits, real-world use cases, and emerging trends shaping the future.
Whether you are an enterprise leader planning cloud adoption or a startup looking to scale efficiently, this guide will help you understand how virtualization powers modern cloud computing.
What is Virtualization in Cloud Computing?
Virtualization in cloud computing is the process of creating virtual versions of physical computing resources, such as–
- Servers
- Storage
- Networks
- operating systems
Instead of running a single application or workload on a single physical machine, virtualization enables multiple virtual environments to share the same hardware efficiently.
In simple terms, virtualization separates software from hardware. Physical resources like CPU, memory, and storage are abstracted into virtual resources that can be allocated, scaled, or reassigned as needed. This abstraction makes infrastructure more flexible, efficient, and cost-effective.
At the core of this process are hypervisors and virtual machines (VMs).
- A hypervisor sits between the physical hardware and virtual machines, managing resource distribution and ensuring isolation between workloads.
- Virtual machines act like independent computers, each running its own operating system and applications.
These components form the foundation that enables modern cloud environments to deliver scalable and on-demand computing resources.
What is the Difference Between Virtualization and Cloud Computing?
There is a clear difference between the two terms. Although the two concepts are closely related. Understanding this distinction is the basics of virtualization in cloud computing and helps clarify how modern cloud platforms work.
- Virtualization is a technology, while cloud computing is a service model built on top of that technology.
- Virtualization enables efficient use of hardware, whereas cloud computing delivers virtualized resources over the internet.
- The need of virtualization in cloud computing arises because cloud platforms rely on it to deliver scalability, flexibility, and multi-tenant access.
Key Differences at a Glance
| Aspect | Virtualization | Cloud Computing |
| Definition | Technology that creates virtual resources | Model for delivering IT services online |
| Purpose | Optimize and abstract hardware | Provide scalable, on-demand services |
| Dependency | Can exist without cloud | Relies on virtualization technology in cloud computing |
| Scope | Infrastructure-level | Infrastructure, platform, and software services |
In short, virtualization enables cloud computing, but cloud computing goes beyond virtualization by adding automation, self-service, and managed delivery.
Role of Virtualization in Cloud Computing
Virtualization in cloud computing enables efficient use of physical infrastructure. It allows multiple workloads to operate independently on shared hardware, reducing costs while improving performance and flexibility.
This abstraction of resources makes it possible for cloud providers to deliver scalable and reliable cloud computing services without requiring users to manage underlying hardware complexities.
Key roles of virtualization in cloud computing include:
- Enables optimal utilization of servers, storage, and network resources
- Supports rapid scaling of applications based on real-time demand
- Improves workload isolation and system reliability
- Reduces infrastructure and operational costs
- Allows faster provisioning and deployment of cloud resources
These capabilities make virtualization essential for building agile, secure, and cost-effective cloud environments.
How Cloud Virtualization Works?
Cloud virtualization enables multiple virtual environments to run on shared physical infrastructure by abstracting hardware resources. This approach is the foundation of virtualization in cloud computing, allowing cloud platforms to scale efficiently while keeping resource management simple and flexible.
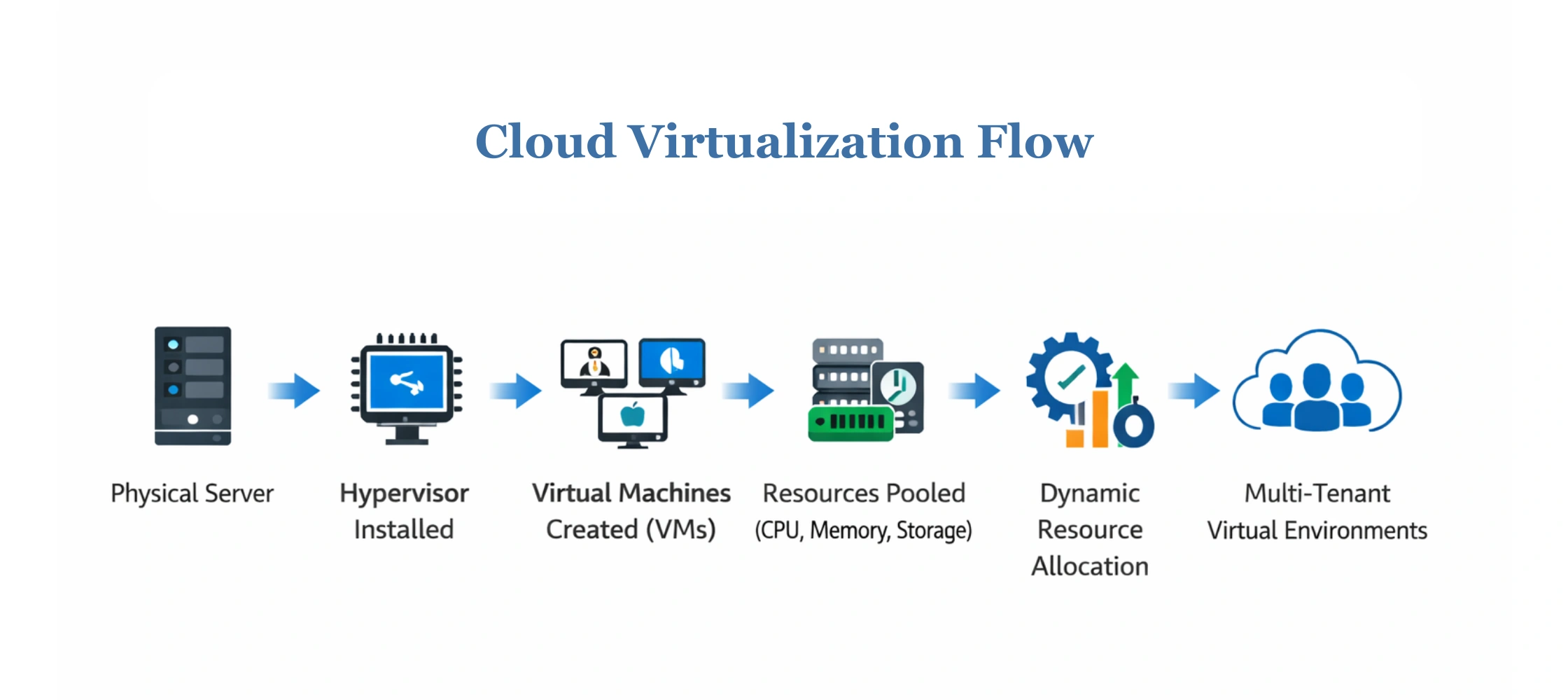
- The process begins with a physical server that provides CPU, memory, storage, and networking resources.
- A hypervisor is installed on this server to manage and divide these resources. It creates and runs multiple virtual machines, each operating as an independent system with its own operating system and applications.
- In cloud computing virtualization, resources from one or more servers are pooled into a shared resource group instead of being fixed to one machine.
- Cloud platforms automatically assign CPU, memory, and storage to workloads based on real-time demand and take them back when not needed.
- Multiple users share the same infrastructure, but each user operates in an isolated virtual environment, ensuring security, privacy, and consistent performance.
Levels and Techniques of Virtualization in Cloud Computing
The levels of virtualization describe how computing resources are abstracted across layers to create flexible, efficient cloud environments. Each level uses specific virtualization techniques in cloud computing to balance performance, scalability, and resource isolation based on workload requirements. Let’s look at them in more detail.
-
Hardware-Level Virtualization
This level uses a hypervisor installed directly on physical hardware to create multiple virtual machines. Each virtual machine runs its own operating system and applications while sharing the same physical server. It is widely used in enterprise cloud environments for strong isolation and resource control.
-
OS-Level Virtualization
OS-level virtualization allows multiple isolated environments to run on a single operating system kernel. Instead of full virtual machines, it uses containers, making it lightweight and ideal for rapid deployment and scalable applications.
-
Application-Level Virtualization
At this level, applications are separated from the host operating system. Applications run in isolated environments without traditional installation, simplifying updates, maintenance, and cross-system compatibility.
-
Full vs Para-Virtualization
Full virtualization completely emulates hardware, enabling unmodified operating systems to run in virtual machines. Para-virtualization improves performance by allowing the guest operating system to communicate directly with the hypervisor.
These levels of virtualization in cloud computing, along with associated techniques, enable cloud platforms to optimize performance, reduce overhead, and efficiently support diverse workloads.
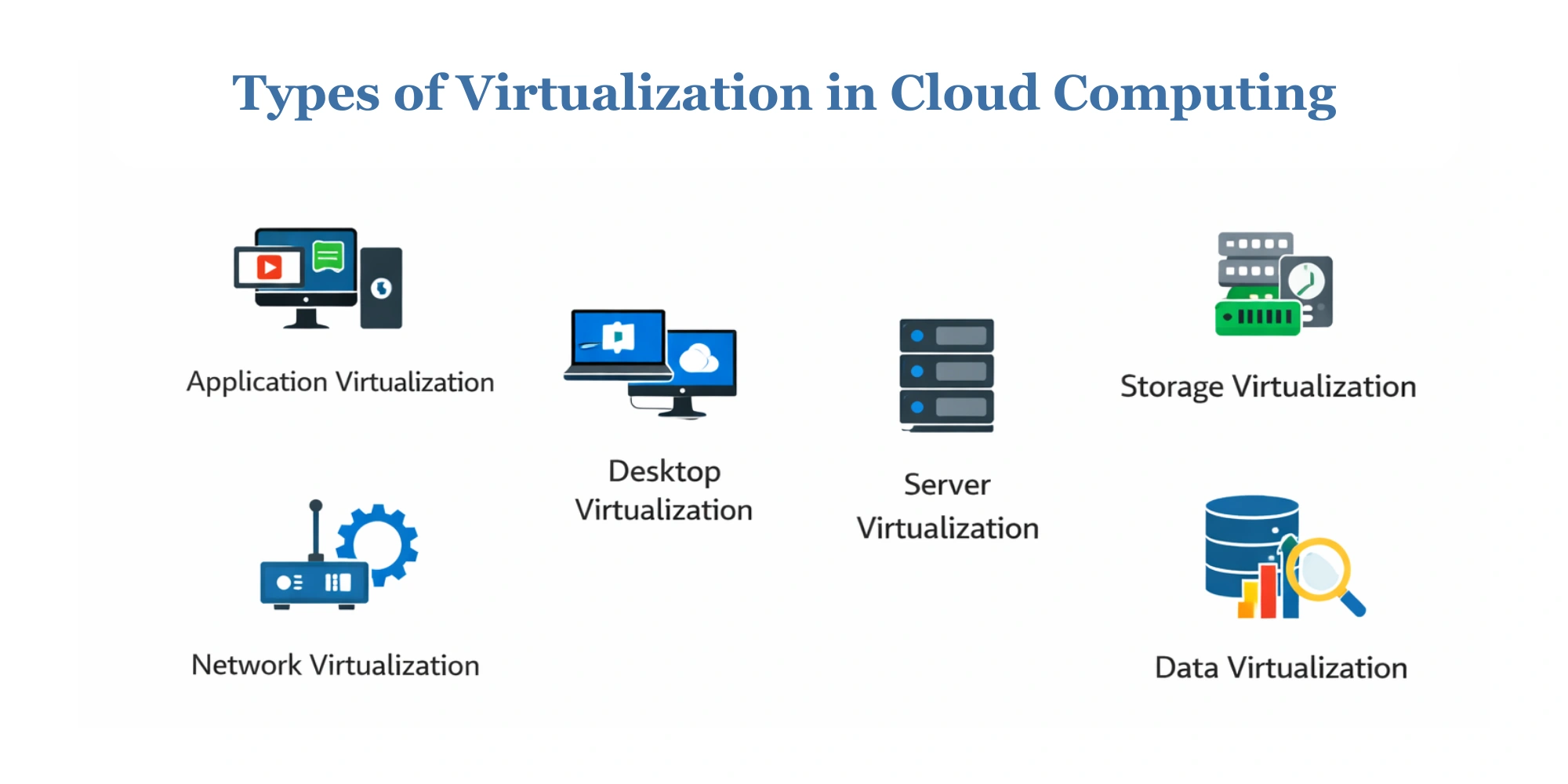
Types of Virtualization in Cloud Computing
Cloud virtualization supports diverse workloads by abstracting servers, applications, networks, desktops, and data into flexible virtual environments. Each type addresses a specific operational need. Let’s look at the types of virtualization in cloud computing.
-
Application Virtualization
Application virtualization in cloud computing allows applications to run without being installed directly on a local operating system. Instead, apps are streamed or executed in isolated virtual environments, making deployment faster and easier to manage.
This approach simplifies updates, reduces compatibility issues, and enables centralized control over applications. As a form of software virtualization in cloud computing, it plays a key role in modern cloud application development, where teams need to deploy and scale applications quickly across different environments.
-
Desktop Virtualization
It enables users to access virtual desktops hosted on centralized servers. Using Virtual Desktop Infrastructure (VDI), employees can log in from any device while experiencing a consistent desktop environment. Desktop virtualization in cloud computing enables a remote workforce, improves data security, and ensures device independence.
It is especially useful for organizations adopting mobile cloud computing, where employees access business systems from multiple locations and devices without compromising control or compliance.
-
Network Virtualization
This model abstracts physical networking components such as routers, switches, and firewalls into virtual equivalents. Using software-defined networking (SDN), network behavior can be configured and managed through software rather than hardware.
Network virtualization in cloud computing enables efficient traffic management, network segmentation, and improved security. Virtual networks can be created, modified, or isolated on demand, making cloud infrastructure more agile and responsive to changing application needs.
-
Storage Virtualization
Storage virtualization in cloud computing pools physical storage from multiple devices into a single virtual storage system. This abstraction enables data to be managed, scaled, and accessed more efficiently, without regard to where it is physically stored.
As part of virtualization in cloud computing, storage virtualization improves performance, simplifies backup and recovery, and ensures better utilization of storage resources across cloud environments.
-
Server Virtualization
It allows a single physical server to run multiple virtual machines simultaneously. Each virtual machine operates independently with its own operating system and applications. Server virtualization in cloud computing maximizes hardware utilization and reduces operational costs.
Google Cloud Computing Services rely heavily on server virtualization to deliver reliable, on-demand computing resources. It improves scalability for data centers and enterprises.
-
Data Virtualization
Many people ask what is data virtualization in cloud computing. So, basically, it provides a unified view of data from multiple sources without physically moving or duplicating it. It enables real-time access to data across databases, cloud platforms, and applications.
Cloud data virtualization reduces data redundancy, accelerates analytics, and supports better decision-making across distributed systems.
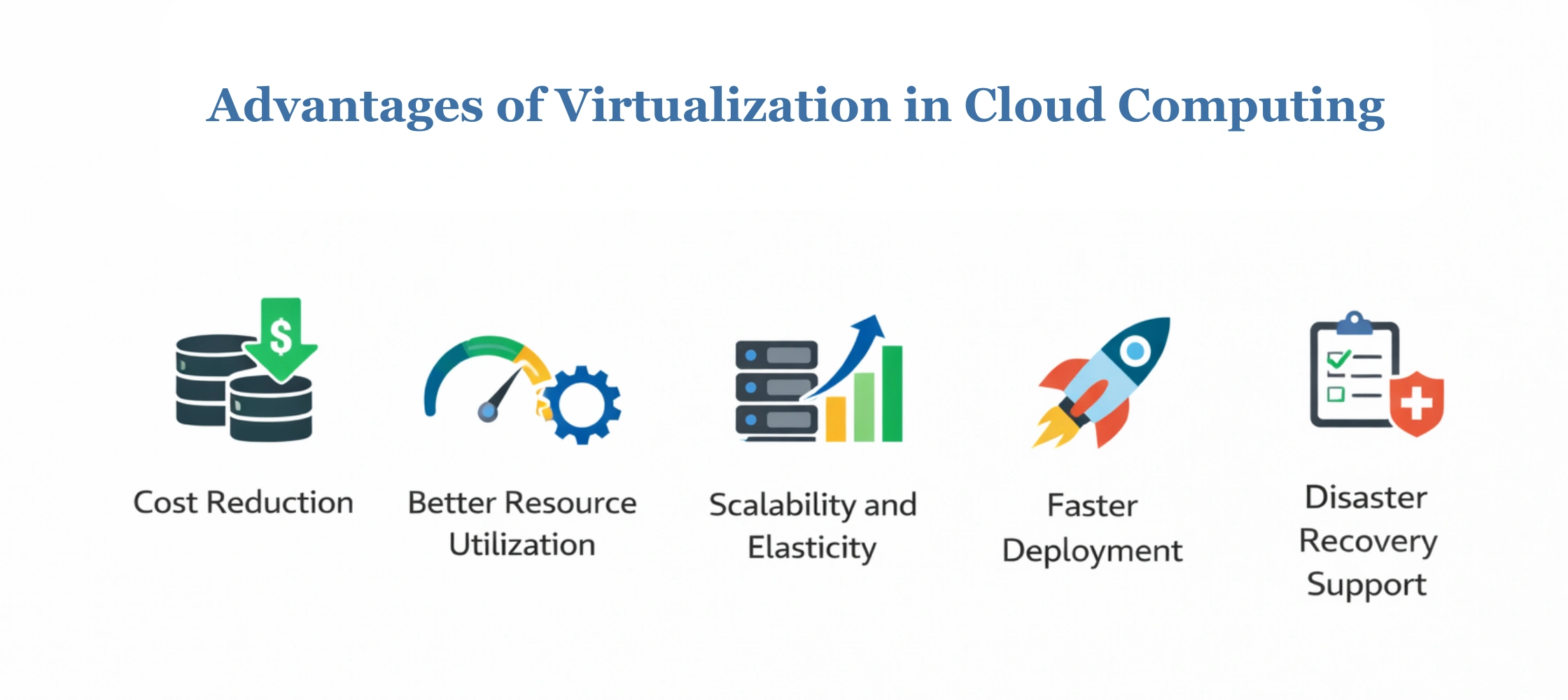
Benefits of Virtualization in Cloud Computing
Virtualization in cloud computing delivers clear business value by helping organizations reduce costs, improve efficiency, and scale with confidence. Cloud virtualization benefits help decision-makers plan long-term digital growth.
-
Cost Reduction
Virtualization reduces capital and operational expenses by allowing multiple workloads to share the same hardware. Organizations can avoid overprovisioning and pay only for the resources they actually use.
-
Better Resource Utilization
Through resource pooling and dynamic allocation, virtualization ensures efficient use of CPU, memory, and storage. Idle resources are minimized, improving overall infrastructure performance.
-
Scalability and Elasticity
Cloud computing virtualization allows resources to scale up or down automatically based on workload requirements. This elasticity helps businesses handle traffic spikes and seasonal demand without manual intervention.
-
Faster Deployment
Virtual environments can be provisioned in minutes rather than weeks. This accelerates application launches, development cycles, and time-to-market.
-
Disaster Recovery Support
Virtualization simplifies backup, replication, and recovery processes. Workloads can be restored quickly in the event of failures, and integration with cloud data security services strengthens data protection and business continuity.
Real-World Examples of Virtualization in Cloud Computing
Use cases for virtualization in cloud computing demonstrate how organizations apply virtualized environments to address real operational challenges. Let’s look at the examples of using cloud-native virtualization in depth.
-
Enterprise Workload Consolidation
Cloud computing in finance uses virtualization to consolidate multiple workloads onto fewer physical servers. This helps lower costs, improve performance, and maintain high availability for mission-critical systems.
-
SaaS Application Hosting
Virtualization enables reliable and scalable SaaS hosting for organizations operating in cloud computing in healthcare, where compliance, data availability, and performance are essential.
-
Development and Testing Environments
Development teams rely on virtual machines to quickly create isolated testing environments. This accelerates development cycles, reduces deployment risks, and keeps production systems stable.
These examples highlight the practical value of virtualization in cloud ecosystems.
Future of Virtualization in Cloud Computing
The future is shaped by the need for faster deployment, greater efficiency, and smarter infrastructure management. As cloud environments evolve, virtualization continues to adapt to modern application architectures and dynamic workload demands. Let’s explore the future trends in virtualization for cloud computing.
| Key Trend | Impact on Cloud Environments |
| Shift toward containerization | Containers offer lightweight virtualization, faster startup times, and improved application portability. |
| Serverless and lightweight virtualization | Serverless models reduce infrastructure management and enable event-driven execution. |
| AI-driven resource optimization | AI improves workload placement, scaling decisions, and cost efficiency |
These advancements are driving smarter cloud ecosystems and enabling organizations to adopt cloud transformation solutions that support agility, innovation, and long-term scalability.
Enterprise-Ready Virtualization Technology in Cloud Computing by SparxIT
Enterprises today require cloud environments that are secure, scalable, and built for long-term growth. SparxIT delivers virtualization in cloud computing solutions designed to modernize infrastructure while maintaining performance, compliance, and operational control.
With deep expertise across cloud platforms and virtualization frameworks, we help organizations migrate from rigid cloud systems to virtualized ecosystems that support evolving business needs and enterprise-scale workloads.
How we support enterprise virtualization in cloud computing:
- Design and implement secure, scalable virtualized cloud architectures
- Optimizes resource utilization to reduce operational costs
- Ensure high availability, performance, and disaster recovery readiness
- Integrate virtualization with broader digital transformation services
- Provide ongoing optimization, monitoring, and support
By aligning virtualization strategies with business objectives, SparxIT enables enterprises to build resilient cloud environments that drive efficiency, innovation, and sustainable growth.

Partner with Experts
Frequently Asked Questions
How does cloud virtualization differ from traditional virtualization?








Cloud virtualization is designed for scalability and on-demand access, while traditional virtualization is usually limited to on-premise infrastructure. Cloud environments add automation, remote access, and flexible pricing on top of virtualized resources.
What are the characteristics of virtualization in cloud computing?














The key characteristics of cloud virtualization include resource abstraction, workload isolation, scalability, hardware independence, and improved fault tolerance across shared infrastructure.
What are the features of virtualization in cloud computing?














Core features of cloud computing virtualization include efficient resource utilization, rapid provisioning, centralized management, and support for disaster recovery.
Is virtualization in cloud computing secure?














Yes, when implemented correctly, virtualization security in cloud computing is secure. Isolation between virtual machines, access controls, encryption, and monitoring helps protect workloads and data from unauthorized access.
How does Kubernetes fit into cloud-native virtualization?














Kubernetes in cloud virtualization enables the orchestration of containerized applications. It automates deployment, scaling, and management, making virtualization more lightweight and cloud-native.
How do virtualization tools in cloud computing support IT environments?














Virtualization tools simplify infrastructure management by automating resource allocation, improving scalability, reducing costs, and enabling faster deployment of applications and services.