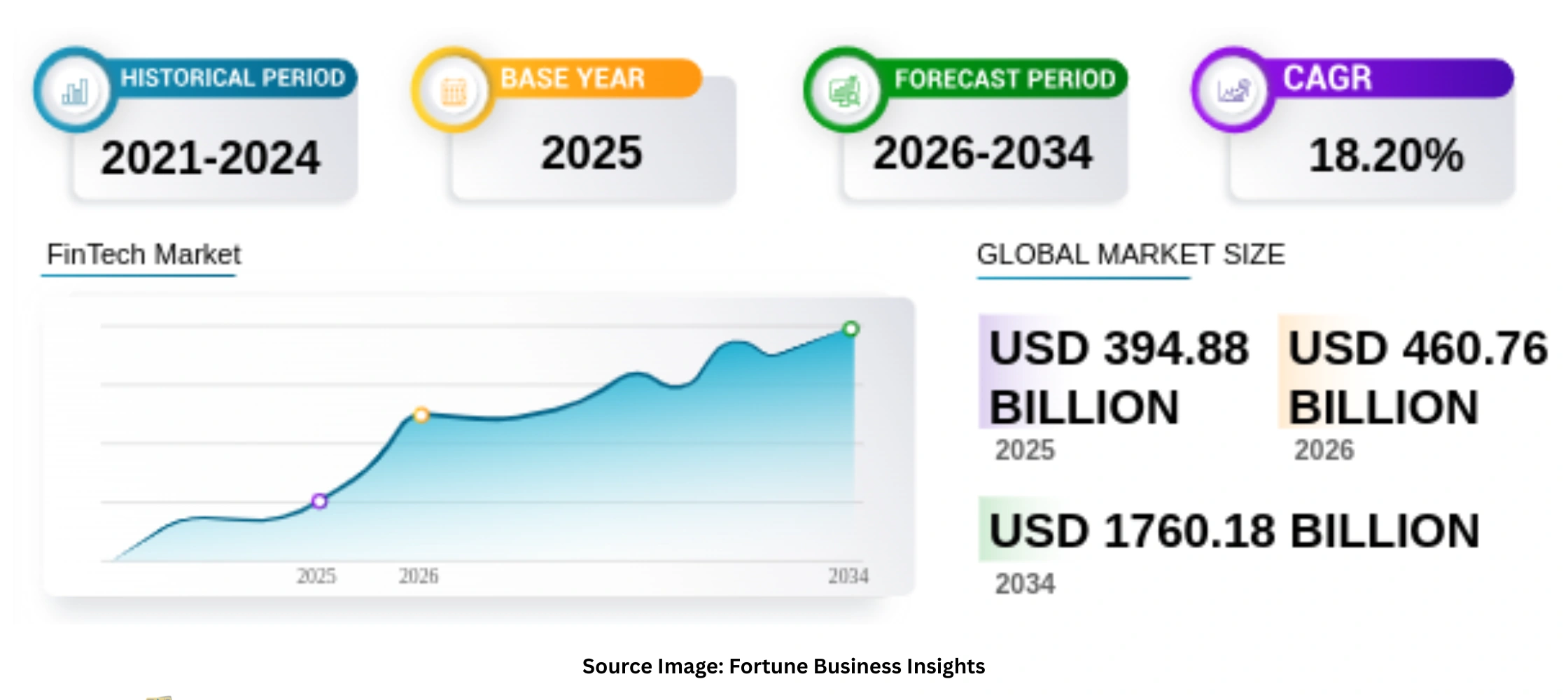
The fintech ecosystem has grown rapidly over the last decade. The global fintech market was worth about $394.88 billion in 2025. It is expected to reach nearly $1760 billion by 2034, growing at a 18.2% CAGR. Digital payments, mobile banking, embedded finance, and real-time transactions are now part of everyday life.
This wave of innovation is driven by digital transformation in banking. It has improved speed and accessibility, but it has also expanded the digital attack surface. As financial platforms become more interconnected and data-driven, securing them has become increasingly complex.
In this environment, cybersecurity in fintech has moved beyond being a backend technical function. It is now a boardroom priority that directly influences business continuity, regulatory standing, and customer trust.
Fintech companies handle vast volumes of sensitive financial and personal data, making fintech cybersecurity essential to protect transactions, prevent fraud, and maintain platform reliability. A single security lapse can lead to financial losses, compliance violations, and long-term reputational damage.
This guide takes a practical look at financial technology security and the challenges it faces. It explains why fintech platforms are attractive targets for cybercriminals, explores emerging threats, and outlines how a structured cybersecurity for financial institutions can help mitigate risks while supporting sustainable growth.
Importance of Cybersecurity in Fintech
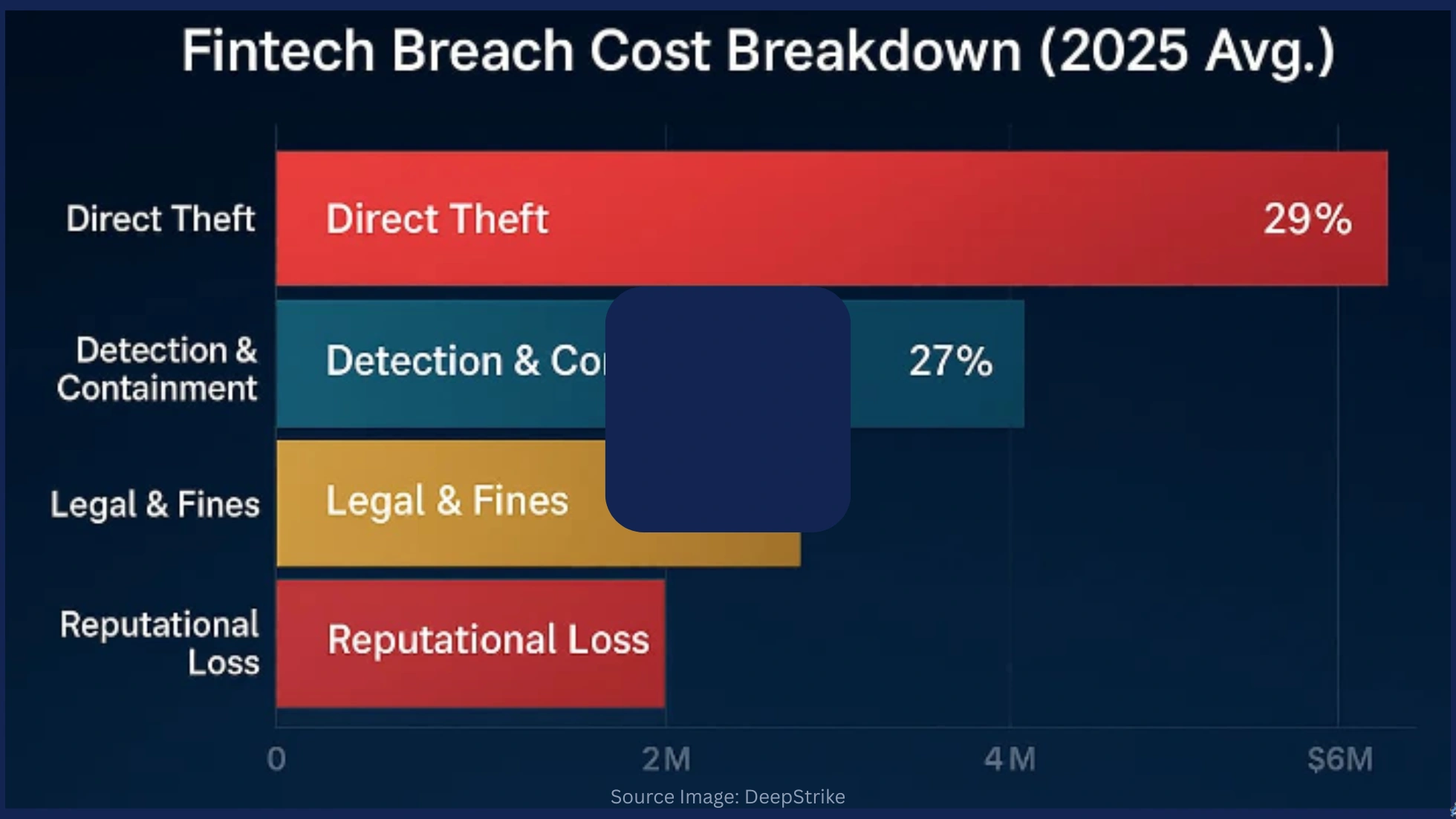
Cybersecurity has become a defining issue for fintech, and the numbers make that clear. Today, fintech companies account for nearly 27% of all reported data breaches, with the average cost of a single incident reaching $5.9 million.
What’s more concerning is that security problems are rarely one-off events. SecurityScorecard research shows that 18.4% of leading fintech firms have experienced public data breaches, and nearly half were hit more than once. This highlights how attackers often return to organizations with unresolved security gaps.
Recent real-world incidents reinforce why cybersecurity in financial services can’t be treated as an afterthought.
- Finastra (UK): In November 2024, early reports from multiple sources pointed to a massive data leak involving nearly 400 GB of bank client records.
- Lemonade (USA): In 2025, a system glitch at the auto insurtech firm exposed 190,000 drivers’ license numbers.
- Revolut (UK): A payment and ATM system glitch led to over $20 million in fraudulent transactions and exposed the personal details of 50,150 users, including names and email addresses.
These incidents underline a simple truth that financial cybersecurity is not just about preventing theft; it is about safeguarding the entire fintech ecosystem. Let’s explore why is cyber security important in finance.
- Protecting sensitive financial and personal data, including bank details, transaction histories, and personal identifiers. Without strong safeguards, these systems face heightened fintech security risks, including unauthorized access and data leaks.
- Building customer trust in digital financial platforms. Users expect fintech applications to meet or exceed the security standards associated with cybersecurity in banking.
- Cyber incidents can trigger severe financial losses, regulatory penalties, and long-lasting damage to a financial brand’s reputation.
- Rather than slowing innovation, robust cybersecurity for finance accelerates growth by reducing security risks and ensuring regulatory readiness.
Why Fintech Companies Are High-Value Targets for Cybercriminals
Fintech companies operate at the intersection of finance and technology. It makes them attractive to cybercriminals seeking quick financial gains, access to sensitive data, and opportunities to exploit digital infrastructure. Let’s explore why fintech institutions have been prime targets for hackers.
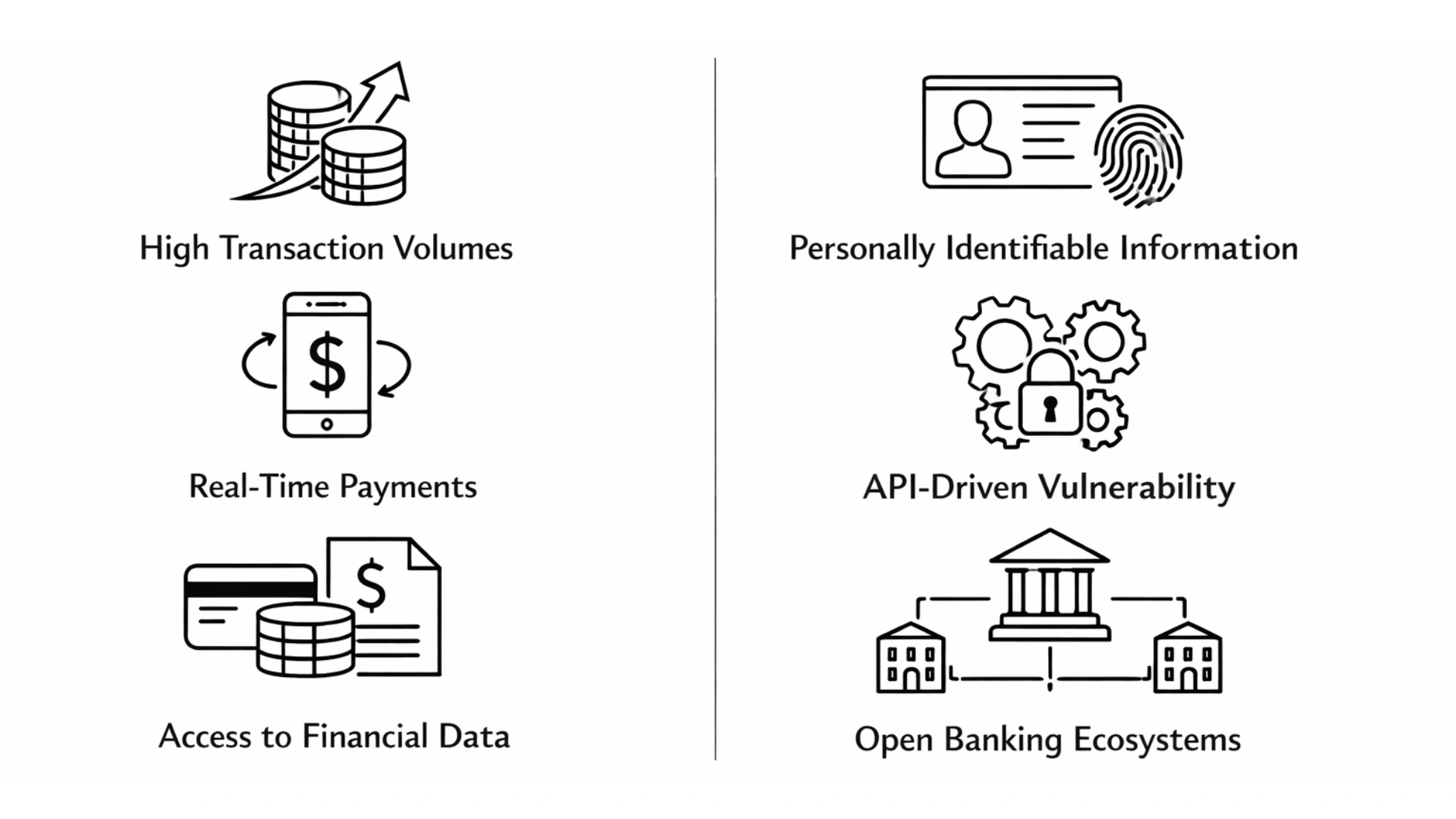
1. High Transaction Volumes and Real-Time Payments
Platforms handling real-time payments are particularly vulnerable because attackers can monetize breaches quickly, increasing the impact of even short-lived security lapses.
- Continuous, high-frequency transactions create multiple entry points for fintech cyber attacks.
- Real-time payment systems leave little room for manual intervention or delayed fraud detection.
- Increased cyber risk & security for financial institutions due to instant fund movement.
2. Access to Financial Data and Personally Identifiable Information
The concentration of financial and identity data makes fintech platforms lucrative targets for large-scale data exfiltration attacks. For example, Slim CD UK payment processor leaked 1.7M credit card numbers and expiry dates.
- Storage of sensitive customer data increases the risk of financial data theft
- Personally identifiable information is a prime target for identity fraud and resale
- Breaches often result in large-scale fintech data breaches that affect multiple user accounts.
3. API-Driven Vulnerability and Open Banking Ecosystems
As fintech platforms increasingly rely on cloud computing in banking, poorly secured APIs can expose entire systems, underscoring the need for proactive threat surface reduction strategies.
- Extensive API usage expands the overall Fintech attack surface
- Open banking integrations increase dependency on third-party systems
- Misconfigured interfaces heighten digital asset vulnerability
Emerging Cybersecurity Threats in Fintech
Fintech platforms operate in highly connected digital environments, exposing them to a new generation of sophisticated attack methods. As systems grow more complex, cyber security threats to the financial sector continue to evolve in scale, speed, and impact.
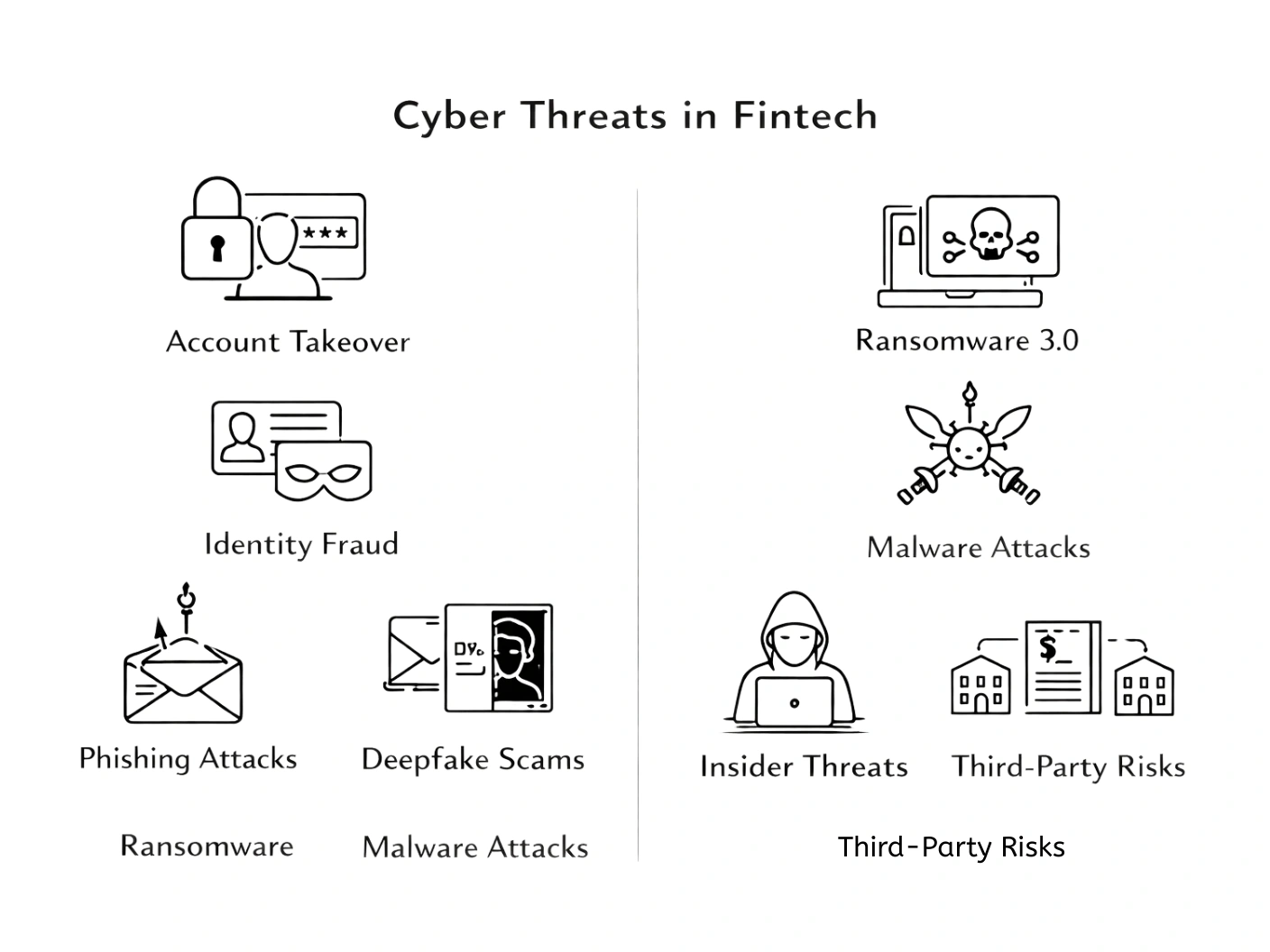
1. Account Takeover and Identity Fraud
Account takeover attacks directly undermine digital payments security, allowing fraudsters to operate under legitimate user identities while evading traditional detection methods.
- Credential stuffing and brute-force attacks remain common entry points
- Synthetic identities and stolen credentials drive identity fraud in fintech
- Compromised accounts enable unauthorized transactions and fund diversion
2. Phishing, Social Engineering, and Deepfake Scams
As social engineering grows more sophisticated, traditional controls are no longer sufficient. Organizations are increasingly adopting phishing-resistant MFA to strengthen fintech cybersecurity efforts across user and employee accounts.
- Highly targeted phishing attacks in fintech exploit user trust and urgency
- AI-driven phishing increases realism through personalized messages and voice cloning
- Deepfake audio and video scams impersonate executives and customer support
3. Ransomware 3.0 and Malware Attacks
Unlike earlier variants, ransomware 3.0 prioritizes business disruption and reputational damage, making recovery more complex and costly.
- Modern ransomware targets cloud infrastructure and backup systems
- In May 2025, Coinbase faced a ransomware attack that leaked limited customer data, leading to a $20 million ransom demand, though no funds were stolen.
- Malware is used to gain persistence and exfiltrate sensitive information
4. Insider Threats and Third-Party Risks
As fintech ecosystems expand, managing insider access and vendor security becomes critical to reducing overall risk and maintaining platform resilience.
- Privileged insiders may misuse access intentionally or unintentionally
- Cash App insiders accessed account IDs and portfolio details of 8.2 million users.
- A SecurityScorecard study found that 41.8% of fintech data breaches are caused by third-party vendors.
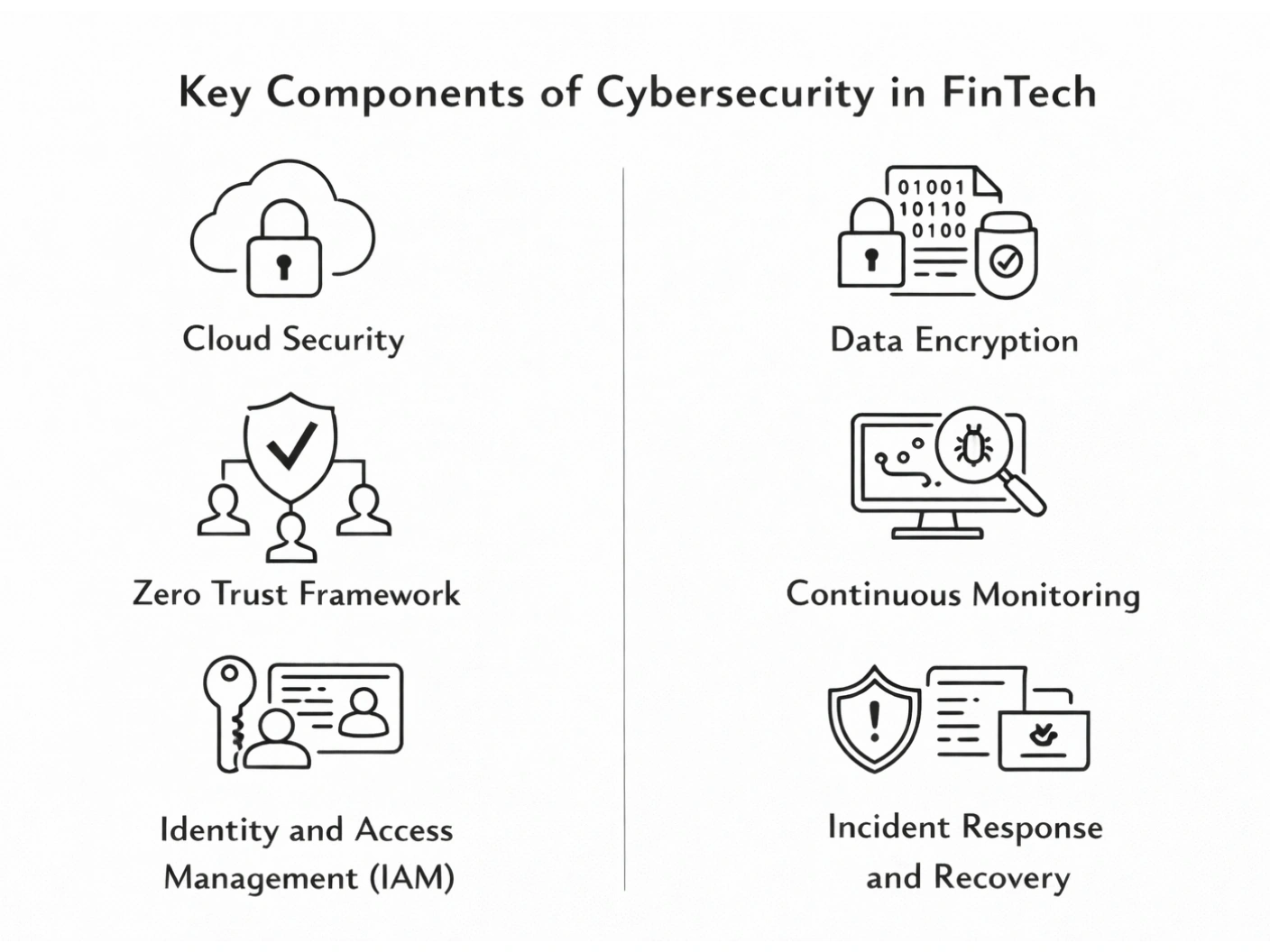
Core Components of Fintech Cybersecurity
A strong fintech security posture is built on layered defenses that protect infrastructure, data, and identities. A well-planned fintech cybersecurity architecture enables scalability, resilience, and regulatory readiness in dynamic digital environments.
-
Secure Infrastructure and Cloud Security Controls
Modern fintech platforms depend on cloud-native systems, making cloud security fintech practices essential. Hardened configurations, network segmentation, and continuous patching help maintain a secure cloud infrastructure that supports high availability without increasing risk.
-
Zero Trust Framework
Zero Trust architecture replaces implicit trust with continuous verification. By validating every user, device, and request, this model strengthens the overall cybersecurity in finance and limits lateral movement across interconnected systems.
-
Identity and Access Management (IAM)
Effective identity access management ensures that users and systems have only the permissions they need. Controls such as multi-factor authentication for finance reduce credential-based attacks and help contain insider risks.
-
Data Encryption and Secure Storage
Strong data encryption methods protect sensitive information at rest and in transit. Secure key management and encrypted storage safeguard financial and personal data, even if systems are compromised.
-
Continuous Monitoring and Threat Detection
Real-time visibility across applications and infrastructure enables early threat identification. API security gateways play a critical role by monitoring interface traffic and preventing unauthorized access.
-
Incident Response and Recovery Planning
Preparedness is essential when incidents occur. Defined response plans, regular application testing, and collaboration with top cybersecurity consulting companies help fintech organizations recover quickly while minimizing operational and reputational damage.
How to Develop a Secure Fintech Application?
Building a secure fintech product starts long before the first line of code is written. A thoughtful, security-first approach ensures your application remains compliant, resilient, and trusted as it scales. Let’s look at the step-by-step mobile app development process to build a fintech app.
-
Security-First Requirement Analysis
Every successful fintech application development journey begins with clear requirements. Security, compliance, and risk considerations should be defined alongside business goals. By adopting shift-left security, teams can identify potential threats early and avoid costly fixes later in the development cycle.
-
UX/UI and Authentication Design
Strong fintech app security does not have to come at the cost of usability. Simple, intuitive mobile app design combined with robust authentication helps protect users without friction. Thoughtful design choices reduce user errors while strengthening cyber security in the financial sector.
-
API and Backend Development
APIs and backend services form the core of modern fintech platforms. Applying secure API development practices, validating inputs, and enforcing strict access controls are essential to maintaining reliable security in fintech software development across interconnected systems.
-
Penetration Testing and Vulnerability Assessment
Regular penetration testing for finance applications helps uncover weaknesses before attackers do. Testing should be performed throughout development and after major updates to ensure new features do not introduce hidden risks.
-
Deployment and Continuous Monitoring
Security does not end at launch. Embedding controls throughout the DevSecOps lifecycle enables continuous monitoring, rapid detection, and faster response to emerging threats. Leveraging the right FinTech app development tools helps teams maintain visibility and protect applications in real-world environments.
App Development Cost for Cybersecurity in Fintech
Cybersecurity is no longer an optional add-on in fintech app development. The overall fintech app development cost ranges from $25,000 to $120,000+, which is strongly influenced by how security is planned, implemented, and maintained throughout the product lifecycle.
Factors Influencing Fintech Cybersecurity Costs
The cost of creating a secure fintech application depends on several variables, including
- App complexity
- Transaction volume
- Data sensitivity
- Regulatory scope
A simple payment app requires fewer security layers than a multi-feature financial platform, directly affecting the fintech app cost.
| App Complexity | Estimated Development Cost | Security Scope |
| Basic Fintech App | $25,000 – $40,000 | Standard authentication, basic encryption, limited compliance |
| Medium Complexity App | $40,000 – $70,000 | Advanced access controls, compliance alignment, and regular testing |
| Advanced Fintech App | $70,000 – $120,000+ | Enterprise-grade security, continuous monitoring, multi-layer compliance |
Balancing Security Investment and Business Growth
Investing in security early reduces long-term risk, builds trust, and improves financial app ROI. Understanding the upfront cost of FinTech app development enables fintech companies to plan forscalable security without slowing innovation.
Challenges in Implementing Fintech Cybersecurity and Their Solutions
Implementing strong protection in fast-moving fintech environments is complex. Let’s look at the common challenges in implementing cybersecurity in fintech that require structured, practical, and scalable responses.
Challenge 1: Integrating Security with User Experience
One of the most common cybersecurity issues in fintech friction. It leads to slower onboarding and a poor user experience.
Solution: Adopt a frictionless authentication approach, such as adaptive MFA and behavioral signals, to maintain security without disrupting user journeys.
Challenge 2: Managing Third-Party and Vendor Risks
Dependence on external APIs, cloud providers, and payment partners increases exposure across the ecosystem.
Solution: Implement structured third-party risk management programs with regular audits and security benchmarks to reduce inherited vulnerabilities.
Challenge 3: Keeping Up with Evolving Threats
Cybersecurity threats to the fintech industry evolve faster than many internal teams can handle, often due to a widening talent gap.
Solution: Leveraging cybersecurity solutions for financial institutions enables early detection and informed response to emerging attack patterns.
Challenge 4: Scaling Security with Business Growth
As fintech platforms scale, security controls that worked initially may fail under higher transaction volumes and user loads.
Solution: Deploying adaptable financial cybersecurity solutions embedded throughout financial services software development processes ensures that protection scales with the business.
Regulatory and Compliance Requirements in the Fintech Industry
Regulatory compliance defines how fintech platforms secure data, manage risk, and operate responsibly. Meeting these standards is essential for protecting users, avoiding penalties, and sustaining trust in digital financial services.
-
PCI DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard)
PCI DSS in Fintech applies to platforms that process, store, or transmit cardholder data. It outlines strict fintech compliance requirements around encryption, access control, network security, and regular testing to reduce payment fraud and data exposure.
-
DORA (Digital Operational Resilience Act)
The DORA regulations focus on strengthening the ability of financial institutions to withstand and recover from cyber disruptions. They emphasize ICT risk management, incident reporting, and resilience testing as core elements of fintech regulations security.
-
Financial Data Privacy and Protection Laws
Financial data privacy laws govern how fintech platforms collect, store, and process customer information. Strong PII (Personally Identifiable Information) protection and transparent consent mechanisms are central to maintaining data privacy in fintech while meeting regional legal obligations.
-
AML and KYC Regulatory Requirements
AML/KYC regulations require fintech companies to verify user identities, monitor transactions, and prevent financial crimes. These controls directly influence system architecture and ongoing security operations.
-
Compliance Enablement Through Technology
Achieving consistent fintech cybersecurity compliance at scale is increasingly supported by RegTech automation, which simplifies audits and reporting. Partnering with the best banking software development companies helps fintech firms embed compliance into their platforms from the outset.
Best Practices for Building a Resilient Cybersecurity Fintech Strategy
Building long-term resilience in fintech requires more than isolated security controls. A structured, proactive approach helps organizations manage risk, respond to incidents effectively, and maintain trust in dynamic digital environments.
Adopt a Zero-Trust Security Model
A Zero-Trust approach strengthens fintech cybersecurity best practices by minimizing the impact of compromised credentials.
- Apply zero-trust fintech principles by verifying every user and request
- Limit lateral movement through micro-segmentation
Implement Multi-Factor Authentication
Multi-factor authentication plays a central role in financial cybersecurity risk management, especially for platforms handling sensitive financial data.
- Enforce strong identity verification across user and admin accounts
- Reduce account takeover and credential abuse
Regular Security Audits and Risk Assessments
Regular audits support an effective incident response plan by improving preparedness and visibility.
- Conduct routine vulnerability scans and application security assessments.
- Identify gaps before they escalate into incidents
Employee Security Awareness and Training
Well-informed employees are critical to executing a sustainable cyber resilience strategy.
- Train teams to recognize phishing and social engineering
- Reduce human error across operations
Continuous Improvement and Security Governance
Embedding these practices throughout financial application development ensures fintech platforms remain secure, compliant, and resilient as they scale.
- Establish clear governance and accountability
- Maintain secure recovery mechanisms such as immutable backups
Real-World Examples of the Best Fintech Applications
Leading fintech companies show that strong security foundations can support innovation without slowing growth. Their real-world implementations highlight how security-first thinking drives trust, adoption, and long-term success.
Top Leading Fintech Companies in the US
- PayPal: It prioritizes risk-based authentication, real-time fraud monitoring, and encrypted payment flows to protect millions of daily transactions. Its layered security model supports secure financial transactions across global markets.
- Stripe Dashboard: Widely recognized for its developer-first approach and robust cybersecurity in FinTech. Strong API protection, automated compliance checks, and continuous monitoring make it one of the most reliable fintech app examples for online payments.
- Chime: This app focuses heavily on consumer protection through instant transaction alerts, account activity monitoring, and proactive fraud detection. These measures position it among the best banking apps for security in the consumer fintech space.
These fintech success stories demonstrate practical use cases of fintech applications, offering clear takeaways for startups aiming to build trust-driven, secure platforms from the start.
Future Trends in Cybersecurity for Fintech
Cybersecurity in fintech continues to evolve as technology advances and threat actors become more sophisticated. Understanding cyber security trends in financial services helps organizations prepare for the future while maintaining trust and resilience.
-
AI-Driven Cybersecurity and Fraud Detection
AI in financial security solutions analyzes massive volumes of data in real time, enabling faster detection of fraud patterns and more adaptive defenses. AI Agent models can autonomously respond to risks, reducing reaction time and human error.
-
Behavioral Biometrics and Passwordless Authentication
Behavioral biometrics analyzes user behavior, such as typing patterns and device interactions, to verify identity. This approach supports passwordless authentication while improving accuracy and reducing friction for users.
-
Preparing for the Next Generation of Cyber Threats
Looking ahead, fintech cybersecurity trends include preparing for Quantum-Resistant Cryptography to protect systems from future quantum attacks. Investing in quantum-resistant finance strategies today ensures long-term security as computational capabilities evolve.
Why Choose SparxIT for Fintech App Development
Choosing the right technology partner is critical when building secure and scalable fintech products. SparxIT stands out as a trusted FinTech App Development company, delivering security-driven solutions aligned with modern regulatory and user expectations.
- Proven experience in financial cybersecurity solutions with deep domain knowledge
- Delivery of secure fintech software development services backed by compliance-first practices
- Strong focus on identity verification fintech to protect users and transactions
- Expert fintech app developers skilled in building top-notch fintech apps.
With end-to-end cybersecurity in fintech expertise, we support businesses from strategy development and design to deployment and ongoing maintenance. Our developers ensure security, performance, and long-term growth that are built into every solution.

Partner with Experts
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the biggest cybersecurity threats to fintech?







Fintech companies face advanced threats such as AI-driven phishing, account takeover attacks, ransomware targeting cloud infrastructure, API abuse, and insider threats amplified by third-party integrations.
How does Zero Trust Architecture improve fintech security?












Zero Trust Architecture improves security by verifying every user and request continuously. This approach limits lateral movement, reduces insider risk, and protects fintech systems from credential-based attacks.
Is it safe to use fintech apps for large financial transactions?












Yes, when fintech apps use strong encryption, multi-factor authentication, real-time monitoring, and secure infrastructure, they can safely support large and high-value financial transactions.
What are the mandatory compliance requirements for fintech startups?












Fintech startups must comply with regulations such as PCI DSS, data privacy laws, AML/KYC requirements, and regional operational resilience standards, depending on where they operate.
How can AI-powered tools prevent financial fraud in real-time?












AI-powered tools analyze transaction behavior instantly, detect anomalies, and block suspicious activity in real time, helping fintech platforms prevent fraud before financial losses occur.